Online Income Tax Calculator: Calculate Income Taxes for FY 2020-21
The Union Budget 2020 has left individuals confused with the choice of the tax regime. Both old and new tax regimes require a proper assessment before choosing one. With the help of the income tax calculator, you can gauge the impact of both the tax structures on your income. This calculator will help you estimate your taxes on your income.
What is the Income Tax Calculator?
Paying tax is inevitable, be it an individual or a business. Income tax is levied on the income earned after considering few deductions. With too many tax exemptions and deductions, calculating tax can be complicated.
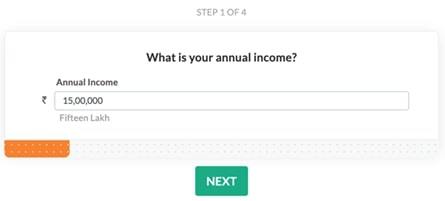
An income tax calculator is a tool that will help calculate taxes one is liable to pay under the old and new tax regimes. The calculator uses necessary basic information like annual salary, rent paid, tuition fees, interest on child’s education loan, and any other savings to calculate the tax liability of an individual.
It gives the total tax payable under the old and new scheme. Also, it suggests investment opportunities for the individual based on the tax liability. The online income tax calculator is a convenient tool and is free to use. It is simple to understand and can be used by anyone to calculate their tax liability.
How does an income tax calculator help you?
The income tax calculator is a very useful tool. It helps to calculate a person’s tax liability by considering necessary details like salary, expenses, and investments. Below listed are the benefits of an income tax calculator.
Tax Planning
The Ministry of Finance in its Union Budget 2020 has given a new tax regime along with the existing one. It’s up to the taxpayers to choose which tax regime they will follow. The income tax calculator will help the taxpayers to access which tax regime best suits them. Individuals can plan their taxes accordingly and avail tax benefit. With tax planning, one can easily do their retirement planning as well. The 80C like NPS and SCSS help in retirement planning.
Easy to Use
The calculator is straightforward to use. The inputs are all investor’s income, expenses, and investment details.
Time-Saving
Planning one’s taxes can be very tiring. And with the introduction of the new tax regime, it has only become complicated. The income tax calculator will help taxpayers calculate taxes under both the regimes and let them decide which one is better for them in a matter of seconds. Hence it saves a lot of time for them.
Free to use
One can use the calculator multiple times at free of cost.
How to use Scripbox's income tax calculator?
Scripbox’s Income tax calculator online helps anyone in determining their tax outflow for the years. The online tax calculator requires some data concerning income, investments, and expenses of the taxpayer to calculate taxes online.
Let us now see the step-by-step process of how one can make use of the Scripbox’s Income Tax calculator online.
Step 1: Enter Annual Income
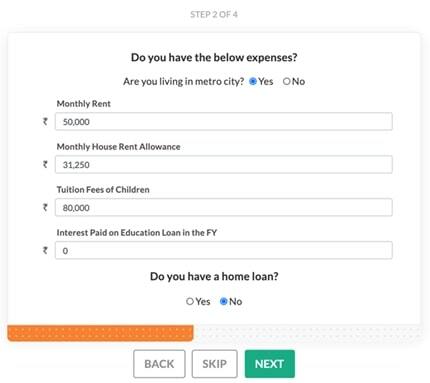
Step 2: Enter Expenses
Here one needs to select whether they are residing in a Metro City or not. Enter Monthly rent paid and rental allowance. Provide children’s tuition fee details, and value of interest paid on Childs Education loan if any. You also have to select whether you have a home loan or not.
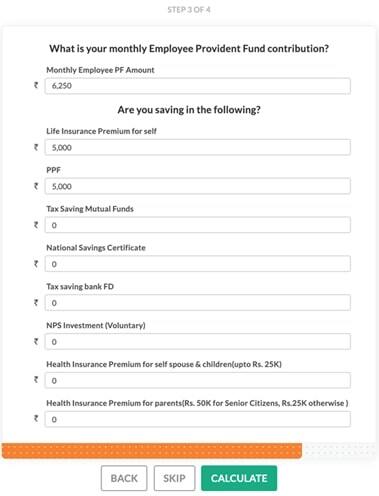
Step 3: EPF and Savings
Here a disclosure of the existing investments has to be done.
Step 4: Calculate
In this step, the calculator calculates the total tax as per the new scheme as well as per the old scheme. Also, it determines how much more needs to be invested for effective tax saving. Furthermore, taxpayers can go back at any step and change the values as required. Additionally, the calculator suggests the best investment options to save tax further.
Benefits of Scripbox's Income Tax Calculator
Following are the benefits of Scripbox’s Income Tax Calculator:
The calculator helps users try various permutations and combinations of investments and expenses to check the tax-flow.
The online tax calculator is completely free. One can calculate their taxes online with Scripbox’s Calculator.
Accurate results are computed within seconds.
The tax calculator online saves quite an amount of time for users from doing lengthy and time-consuming calculations.
Scripbox’s Income Tax Calculator provides investment options for the assessee to save tax further by taking advantage of the deductions.
Also, the calculator helps in investment planning.
What are the Sources of Income?
For income tax calculations, income is categorized under the following five categories:
Income from Salary
It is the monthly income one receives for their work from the employer. Usually, the salary component in a payslip includes the following:
Basic Salary
Dearness Allowance (DA)
Gratuity and Annuity benefits
Allowance: Medical, Transportation, etc.
Any Special Allowance
The total of the above components becomes the Gross Salary of an Employee. Part of the gross salary is subject to taxation after certain deductions.
Income from Business or Profession
It includes the income generated from a business or a professional engagement. This income also becomes part of the taxable income.
Income from Capital Gains
Capital Gains are classified as Short Term Capital Gains (STCG) and Long Term Capital Gains (LTCG). Income from Capital Gains can become tedious to compute at times. The number of transactions and complexity sum up to the effort required to calculate the income. Total sales of all capital assets come under this category.
Income from rent on house property
This mainly consists of rental income received by the taxpayer from the house he let out. In the instance where the assessee resides in the only self-owned house, he is required to compute income from house property. This is usually nil or negative.
Income from other sources
Income from sources that don’t fall under the above four categories become part of the income from other sources. It usually includes interest income, dividend income, gifts (taxable), etc. These components are tracked from the credit entries in the savings account.
Additionally, interest on cumulative Fixed Deposits (FD) is not credited to a savings account. Therefore, an interest certificate needs to be obtained, although the certificate is required only when TDS is not deducted. Use Scripbox's FD calculator to calculator to calculate interest from FD.
How to Calculate Income Tax in FY 2020-21?
Let’s start with the basics here. For a salaried employee, the monthly payslip describes the various components of one’s salary. Have a look at your payslip. You will find that your total salary is the total of Basic Salary HRA Transport Allowance Special Allowance Any other allowance. Income Tax Act provides various exemptions from salary like house rent allowance, leave travel allowance, etc.
Further, budget 2018 also introduced the concept of standard deduction of INR 40,000, which has been again increased in budget 2019 to Rs 50,000. This tax exemption will not be available in case you are opting for the new tax regime.
Before we move to the calculation part, it is essential to know that if you are opting for the new tax regime, many exemptions are not allowed to be claimed.
Exemptions not allowed under the new tax regime
Individual or HUF opting for taxation under the newly inserted section 115BAC of the Income Tax Act shall not be entitled to the following exemptions/deductions:
Leave travel concession as contained in clause (5) of section 10;
House rent allowance as contained in clause (13A) of section 10;
Some of the allowance as contained in clause (14) of section 10;
Allowances to MPs/MLAs as contained in clause (17) of section 10;
Allowance for the income of minor as contained in clause (32) of section 10;
Tax Exemption for SEZ unit contained in section 10AA;
The standard deduction, the deduction for entertainment allowance and employment/professional tax as contained in section 16;
Interest under section 24 in respect of self-occupied or vacant property referred to in sub-section (2) of section 23. (Loss under the head income from house property for the rented house shall not be allowed to be set off under any other head and would be allowed to be carried forward as per existing law);
Additional depreciation under clause (iia) of sub-section (1) of section 32;
Deductions under section 32AD, 33AB, 33ABA;
Various deduction for donation for or expenditure on scientific research contained in sub-clause (ii) or sub-clause (iia) or sub-clause (iii) of sub-section (1) or sub-section (2AA) of section 35;
Deduction under section 35AD or section 35CCC;
Deduction from family pension under clause (iia) of section 57;
Any deduction under chapter VIA (like section 80C, 80CCC, 80CCD, section 80D, section 80DD, section 80DDB, 80E, 80EE, 80EEA, 80EEB, 80G, 80GG, 80GGA, 80GGC, 80IA, 80-IAB, 80-IAC, 80-IB, 80-IBA, etc). However, deduction under sub-section (2) of section 80CCD (employer contribution on account of the employee in notified pension scheme) and section 80JJAA (for new employment) can be claimed.
Exemptions allowed under the new tax regime
Following allowances shall be allowed as notified under section 10(14) of the Act to the Individual or HUF exercising option under the proposed section:
Transport Allowance granted to a divyang employee to meet the expenditure for commuting between residence and place of duty
Conveyance Allowance granted to meet the expenditure on conveyance in performance of duties of an office;
Any Allowance granted to meet the cost of travel on tour or transfer;
Daily allowance to meet the ordinary daily charges incurred by an employee on account of absence from his normal place of duty.
Now that we have discussed the above, we can move onto the practical aspect of the same. We will be calculating the total income and income tax on the same should you choose to go with either the old tax regime or the new tax regime.
Example
Amit receives a Basic Salary of INR 1,20,000 per month. House Rent Allowance is INR 50,000 per month and Special Allowance of INR 30,000 per month. Amit lives in Bangalore and the rent paid per month is INR 30,000. Below is what Amit’s taxable salary would look like:
What are the details required when e-filing income tax returns?
IMPORTANT LINK::;
Click here for Income tax Department official Calculator
Following details are required to e-filing income tax return:
Basic details like PAN, Aadhar card details, permanent address
Details of all the bank accounts held in the financial year. Among these banks account, in which bank account refund amount (if any) must be credited
Income earned proof like Form-16, interest earned on Fixed Deposits (FDs), and other investments.
Deduction claimed under Chapter VI-A proof like LIC receipt, investment, health insurance policies.
Tax paid proof like advance tax paid challan, TDS forms.











No comments:
Post a Comment